Let’s be real—stepping into the world of Building Information Modeling (BIM) for the first time feels like crash-landing in a foreign country where everyone speaks in acronyms, and somehow everyone understands it BUT you.
People are casually throwing out terms like “LOD,” “COBie” and “Clash Detection” like they’re part of some secret BIM cult, and you’re just standing there nodding like a bobblehead, secretly Googling on your phone and wondering if you accidentally signed up for an advanced linguistics class.
Don’t worry, we’ve all been there. Every BIM expert was once a wide-eyed newbie thinking, What on earth is a ‘Revit Family,’ and why does it sound like I’m joining the mob?
In this blog, we’re cutting through the BIMbo jumbo (yes, pun intended) to break down the terms and phrases you’ll hear on Day 1—and help you sound like you’ve been part of the BIM crew all along.
Software
Revit
Revit, made by Autodesk, is a powerful software used for designing, modeling, reviewing, analyzing, and producing documentation for building projects. It allows users to model architectural, structural, mechanical, plumbing, electrical, and fire protection systems all in one place. With Revit, teams can collaborate on a shared model, ensuring everything is aligned and accurate throughout the project’s lifecycle.
Navisworks
Navisworks, made by Autodesk, is your go-to tool for managing and coordinating building projects. It takes 3D models from different software and combines them into one powerful, unified model. From there, you can easily navigate, analyze, and evaluate designs from all kinds of disciplines in one place. Plus, with clash detection, you can spot potential issues before they become expensive problems, making coordination smoother and keeping your project on track.
General Terms
BIM (Building Information Modeling)
BIM (Building Information Modeling) is a digital approach to designing and managing building projects, using 3D models to improve collaboration. It takes all different design plans—like architecture, structure, and MEP—and combines them into one unified model. This integration helps identify problems early, reduces errors, increases accuracy, and helps teams make better decisions. BIM also boosts efficiency, saving time and money by preventing costly mistakes and rework. The goal of BIM is to eliminate clashes and conflicts in the project.
VDC (Virtual Design Construction)
Utilizing BIM to simulate and analyze the construction process.
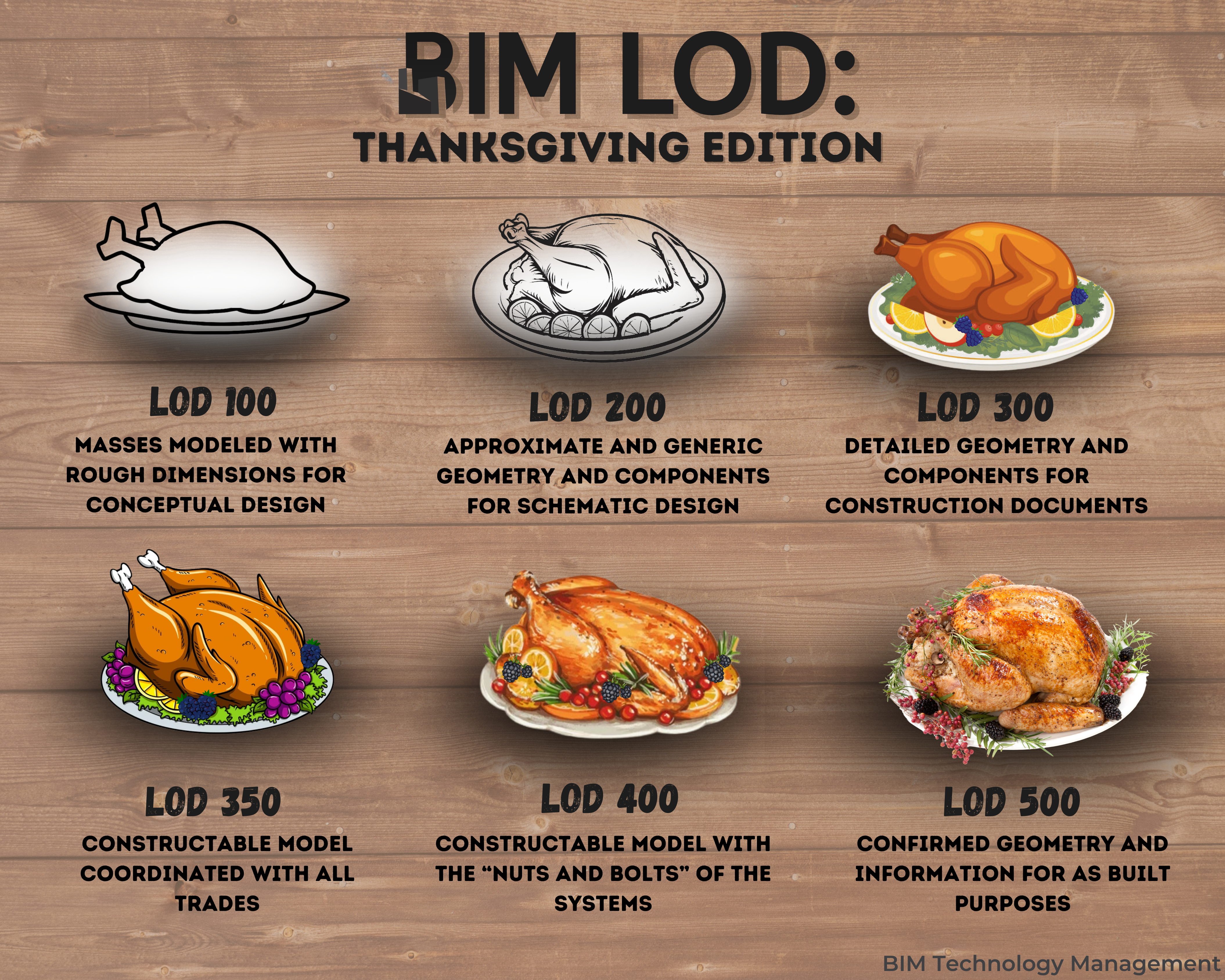
LOD (Level of Detail or Level of Development)
An industry term used to describe where in the project life cycle the BIM is currently at/in. There are levels 100, 200, 300, 350, 400, and 500. BIMTM typically operates in LOD 350 and 400, whereas 100-300 are the design team, and 500 transfers to the building owners. Refer to this handy graphic for a visual representation!
MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing)
The behind-the-scenes systems that make a building operate correctly. Need we say more??
SOW (Scope of Work)
The specialty being addressed or needed for a particular project or task. (electrical, fire protection, mechanical, plumbing, HVAC, etc.)
Family
A Revit based element (2D or 3D) or group of elements with similar characteristics in a model. Families can be parametric, meaning they can be customized based on specific dimensions or requirements.
Parameter
A variable in a BIM model that defines characteristics of an element, like size, material, cost, or performance data. Parameters help customize elements for different project needs.
Parametric design
A feature in Revit that links elements in the model to respond to each other. (Ex: if you change the size of a door, the wall or window placement changes too)
Parametric Modeling
Creating BIM objects and elements with adjustable parameters that can be modified and updated dynamically.
Clash Coordination and Clash Detection
Identifying conflicts and clashes between different building systems and components in a BIM model.
Federated Model
A combined BIM model that integrates various disciplines’ models (architecture, structure, MEP) into a single comprehensive model.
Laser scanning
Using laser technology to capture accurate as-built measurements for BIM modeling.

Point cloud
A collection of data points representing the physical characteristics of a building or site captured by laser scanning. These points can be combined using various software to develop a complete digital representation of the building.
Prefab (Prefabrication)
Building parts made in a factory and then assembled on-site. It’s like buying preassembled furniture—everything’s built off-site and delivered ready to go, saving time and often improving quality and reducing injury.
Quantity Takeoff
Extracting accurate quantities and measurements from a BIM model for cost estimation and material procurement.
Spool
Smaller, broken-down parts of a building that are constructed ahead of time in prefabrication. Spools are often color-coded by the area in the building that they are in to make it easier to sort out on-site.
The spool map is the final deliverable that maps out all the spools in one document. Not every project gets a spool map; it depends on the project requirements and what the contractor wants.

(Take a stretch break, scholar. We’re halfway there, I swear!)
RFI (Request for Information)
A formal question sent during a construction project to clarify details, fill in missing information, or resolve conflicts in the plans.
RFP (Request for Proposal)
Like the name says, it is a request to submit a proposal for the potential project. The RFP includes project requirements like the required completion date or budget, etc.
ROI (Return on Investment)
Measuring the financial benefits and value generated from BIM implementation
Sustainability Analysis
Assessing the environmental impact and energy performance of a building using BIM data
GIS integration
Integrating BIM models with Geographic Information Systems for spatial analysis and data visualization
IPD (Integrated Project Delivery)
A collaborative approach involving multiple stakeholders throughout the project lifecycle
As-built Model
A BIM model reflecting the actual conditions and dimensions of a completed building or structure
FM (Facility Management)
Using BIM data for efficient operation and maintenance of a facility
Asset Management
Managing and maintaining facility assets through BIM data for efficient operations and maintenance
COBie (Construction Operations Building Information Exchange)
A standardized way to organize and share essential building data, like equipment, materials, and maintenance info. Think of it as a super-detailed spreadsheet that helps streamline handover from construction to operations—so you’ll always know what’s installed, where, and how to maintain it.
Digital Twin
A virtual replica of a physical building or infrastructure created through BIM data, allowing for real-time monitoring and analysis
API (Application Programming Interface)
Allowing for integration and data exchange between different software applications.

So, there you have it folks. A beginner’s BIM dictionary to master BIM-ish—packed full of common terms and phrases to help you learn the industry lingo. And I know, I know. “That was way so many terms! How am I supposed to remember all that?!”
Don’t worry, we have a handy downloadable BIM dictionary with these general terms that you will see most commonly. Keep that close by and refer to it when you get confused.
Just remember, everyone starts somewhere. Stick with it, and you’ll be speaking BIM-ish in no time. Stay tuned for trade-specific terms in future blog posts!
Follow us on LinkedIn to know when the next blogs come out, and visit our past blogs here!
Until next time,
— BIMTM


